Products/ Process Gas Chromatographs
The HPGC-1000 Process Gas Chromatograph
The HPGC-1000 Online Process Gas Chromatograph is designed to separate and analyze virtually all gas mixtures or liquid mixtures that can be vaporized. Its specially engineered hardware and software meet stringent requirements for measurement repeatability and long-term stable operation. Featuring a flexible column oven design and modular functional components, this system enables sophisticated analytical applications.
As an industrial-grade process chromatograph, it also complies with environmental monitoring requirements through its precision measurement capabilities and continuous operational reliability.

The HPGC-1000 process gas chromatograph supports three detector configurations for comprehensive analysis:
– Thermal Conductivity Detectors (TCD) measure non-corrosive components like hydrogen and nitrogen
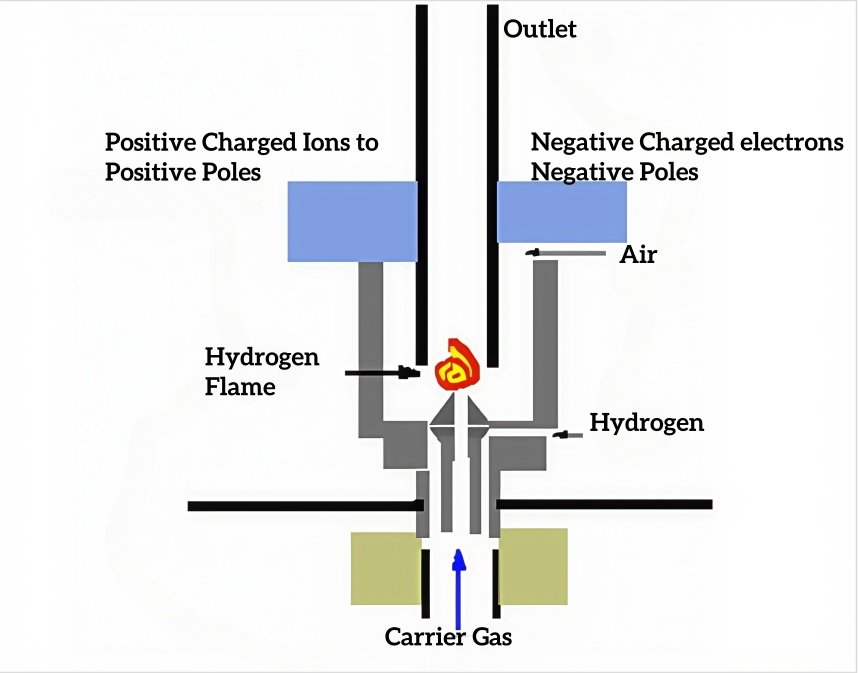
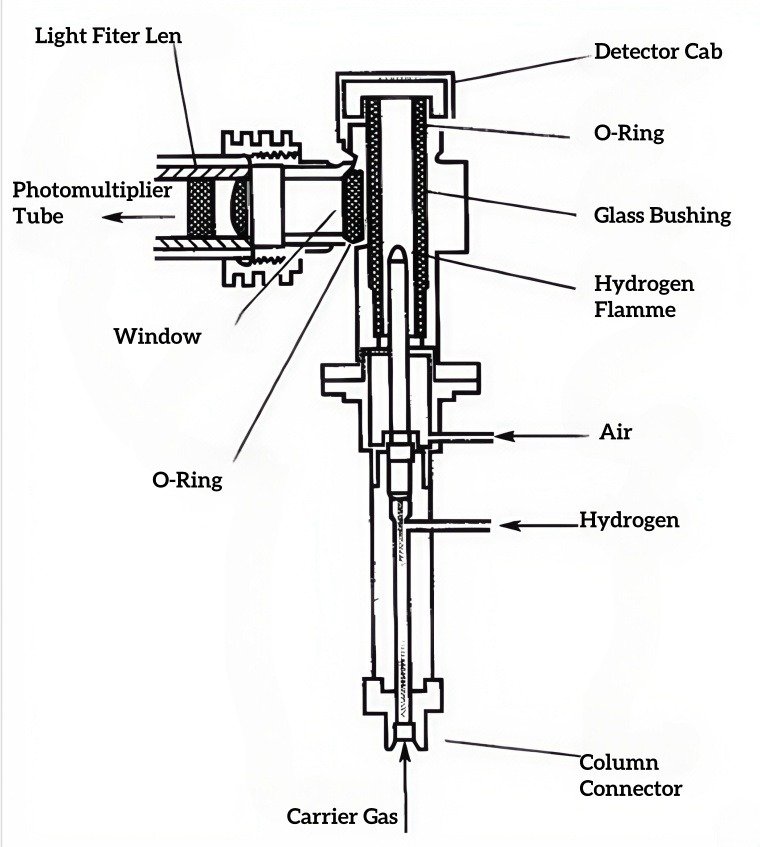
– Flame Ionization Detectors (FID) excel in hydrocarbon quantification
– Flame Photometric Detectors (FPD) specifically target sulfur compounds


| Model | HPGC-1000 | Measurement Object | Gases or vaporizable liquids | Protocol | Modbus RTU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambient Temperature | -10°C to 40°C | Measurement Range | ppb to 100% (depending on the analyte) | HMI | 10.4-inch color touchscreen |
| Detector Types | – TCD – FID – FPD – PDHID | Multi-Detector Capability | Supports simultaneous installation of 2 FIDs or 4 TCDs | Power Supply | – 220 VAC ±10% – 50 Hz ±5% |
| Lower Detection Limits | – FID: 15 ppb (CH₄) – TCD: 100 ppm (CH₄ in H₂) – FPD: 0.1 ppm (H₂S) – PDHID: 10 ppb (CH₄) | Zero Drift | – TCD ≤1% (1 hour) – FID ≤1% (1 hour) – FPD ≤1% (1 hour) – PDHID ≤1% (1 hour) | Dimensions | – N-type: 680 mm (W) × 407 mm (D) × 955 mm (H) – L-type: 770 mm (W) × 407 mm (D) × 1159 mm (H) |
| Repeatability Error | ≤±1% F.S. (varies with application) | Heating Method | PID-controlled air bath heating | Weight | – Explosion-proof: ~100 kg – Non-explosion-proof: ~84 kg |
| Oven Temperature Range | Ambient +10°C to 180°C | Control Accuracy | ±0.05°C | Standard I/O (Expandable as needed) | – Inputs: 8 analog inputs (AI); 8 digital inputs (DI) – Outputs: 12 analog outputs (AO); 8 digital outputs (DO) |
| Thermostatic Chamber Volume | 40L | Sampling Valves | – Diaphragm valve – rotary valve – liquid sample injection valve | Communication Interfaces | – RS-232 – RS-485 – Ethernet |
| Number of Installable Valves | Maximum 10 valves | Column Types | – Packed column – micro-packed column – capillary column | Applications | – Chemical – natural gas – petroleum – metallurgy – industrial gas industries |
| Carrier Gas Pressure | 0.1–0.5 MPa | Accessories | Methane conversion furnace/hydrocarbon remover | Carrier Gas & Consumption | – Flow rate: 30–300 ml/min – Purity: 99.999% N₂/He (compatible with purifiers) – Control Accuracy: ±0.001 psi |
| Instrument Air | – Oil-free, dry – 0.5 MPa – Flow rate: 100 L/min | Explosion-Proof Rating | Ex db eb mb pxb II C T4 Gb | Auxiliary Gases | – Combustion Support: 300–450 ml/min (Zero-grade air) – Fuel Gas: 25–45 ml/min (99.999% H₂) – Drive Gas: N₂ or Air |
CONTROL ANALYTICAL SARL
YOUR ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTION EXPERT!
France Good Quality Portable Syngas Analyzer Supplier. Copyright © 2023-2024 gas-analyser.com . All Rights Reserved.