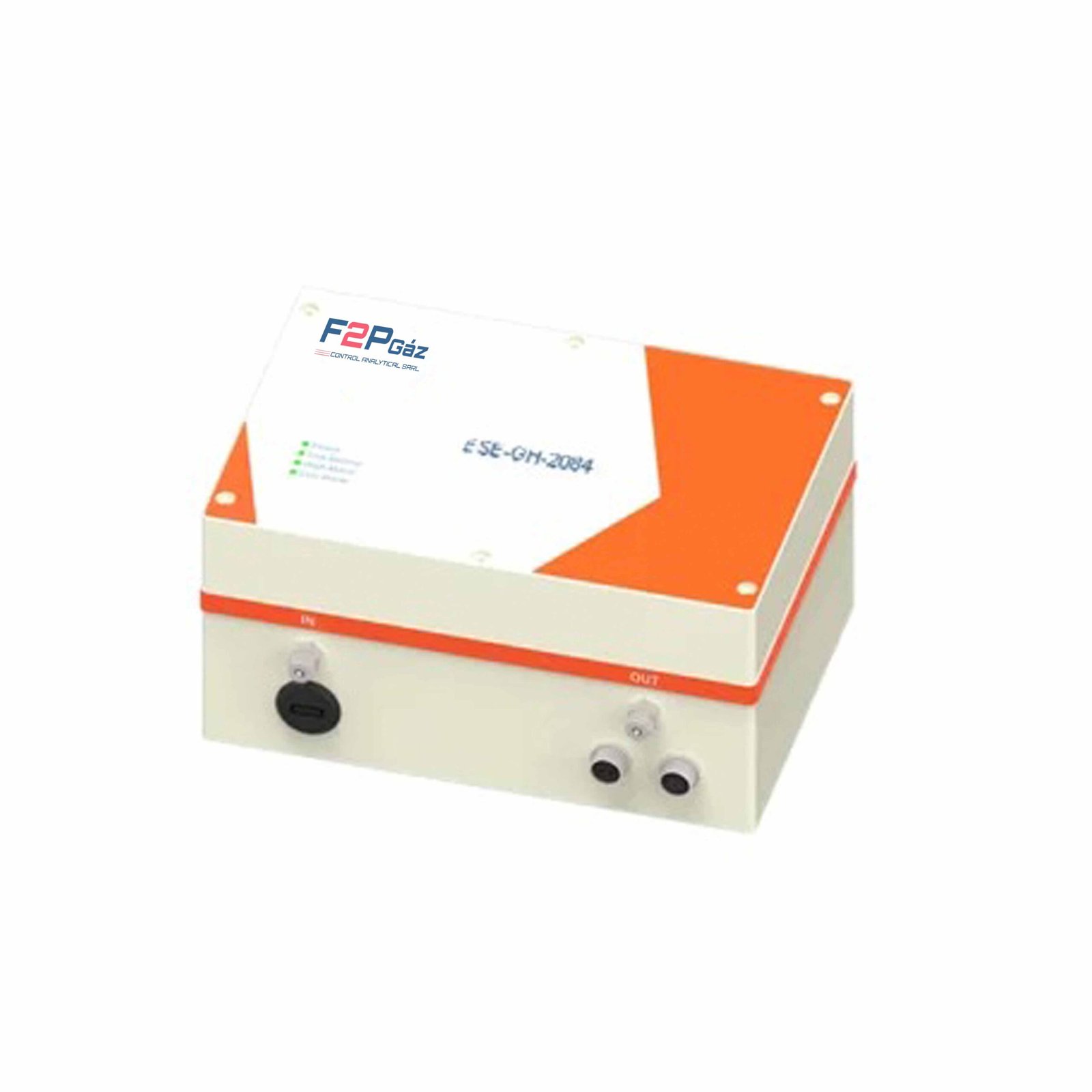
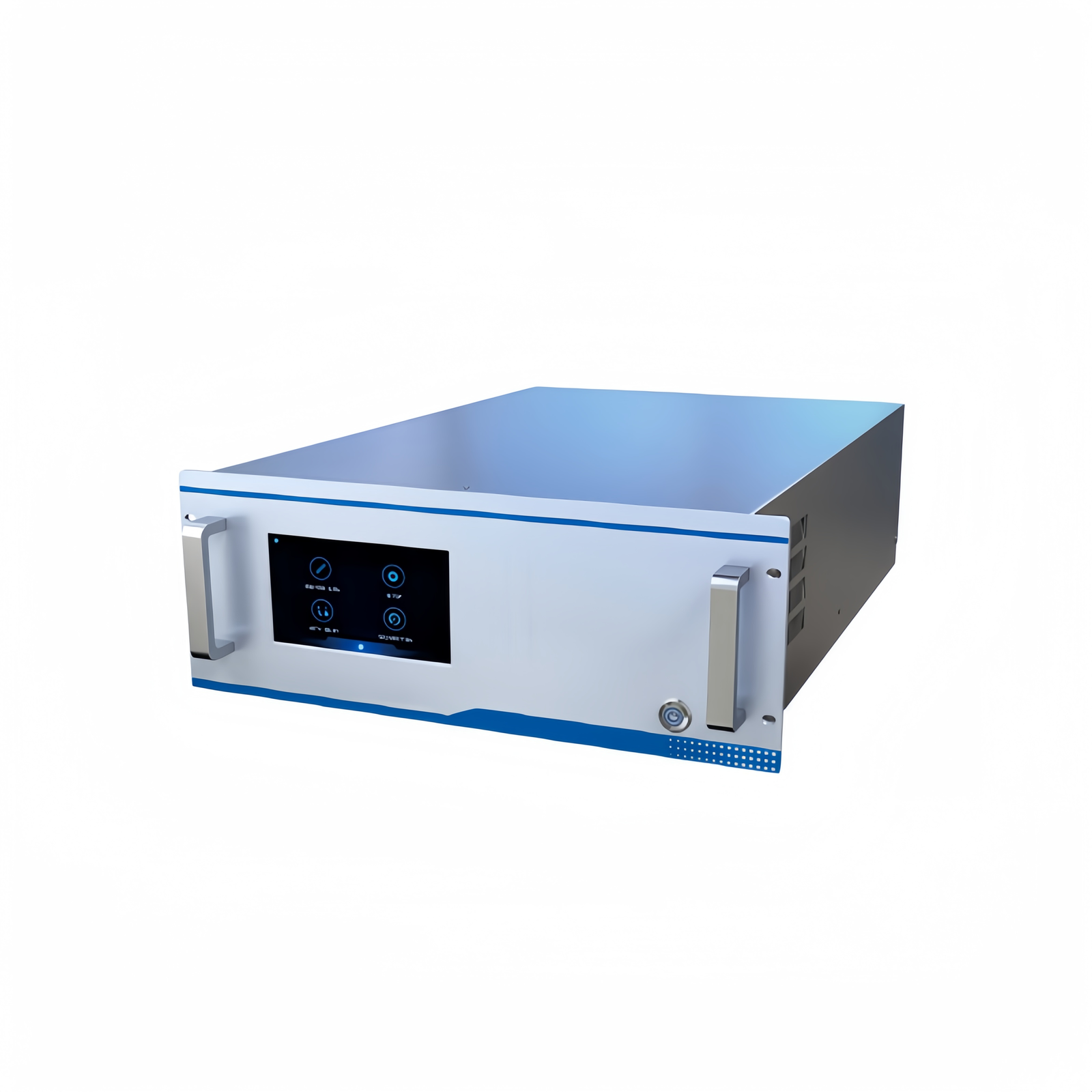
Greenhouse Gas Analyzer
Prosucts/Greenhouse Gas Analyzer
Greenhouse Gas Analyzer
To establish a database for monitoring greenhouse gas concentration changes and a system for estimating, comparing, and verifying carbon emissions from emission sources, we obtain observational data on changes in greenhouse gas concentrations, and further we are able to understand the dynamic changes in greenhouse gas concentrations. Based on the database and system, we can provide scientific and technological support for our purposes, such as the effective evaluation of regional climate change, and the social, economic, and environmental benefits of energy conservation and emission reduction.
All you have to know about Greenhouse Gas Analyzer
A greenhouse gas analyzer is a precision instrument used to monitor and measure the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O). These gases significantly impact global warming and climate change. The analyzer is designed to accurately and rapidly detect these gases’ concentrations, allowing researchers and zenvironmental management agencies to monitor their levels and dynamic changes. It is widely used, from studying the dynamics of greenhouse gases in agriculture and ecosystems to monitoring urban and industrial emissions.
How does the Greenhouse Gas Analyzer work?
The infrared light emitted by the light source enters the gas pool alternately through the GFC modulation wheel. One path is absorbed by the bubbles filled with the gas to be measured, and the other path passes through the bubbles that do not contain the gas to be measured. The two paths of light are respectively gathered by the lens and received by the infrared detector. After signal processing, the measurement signal and reference signal are obtained. By analyzing the two signals, the concentration of the relevant components in the gas can be obtained .
What are the main applications of Greenhouse Gas Analyzer?

In atmospheric monitoring
Governments and research institutions use these devices to monitor greenhouse gas levels across different regions to assess and control emissions’ impact on climate.

In agriculture and forestry
Researchers monitor greenhouse gas fluctuations to understand processes such as photosynthesis in plants, carbon cycling in soils, and their contribution to emissions.

In industrial and environmental sectors
Companies use analyzers to monitor and reduce greenhouse gas emissions in production processes.

In greenhouse cultivation
Farmers use these analyzers to control CO₂ concentrations to promote plant growth and improve crop yields. Additionally, they are indispensable in climate change research, ecosystem carbon balance monitoring, and environmental policy evaluation.
How accurate are Greenhouse Gas Analyzers?
Greenhouse gas analyzers are highly accurate and can typically measure concentrations at parts per million (ppm) or even lower. The accuracy depends on the instrument type and application. For example, high-precision laboratory-grade analyzers can achieve even lower detection limits (e.g., parts per billion or ppb), suitable for micro-gas detection in scientific research, while portable or field-monitoring analyzers may have slightly lower accuracy but still meet most environmental monitoring needs. Measurement accuracy is influenced by factors like sensor type, environmental conditions, and calibration. In environments with temperature and humidity fluctuations, the accuracy might decrease, so compensation for temperature and humidity is usually needed to ensure reliable results.
Do Greenhouse Gas Analyzers require regular calibration?
Yes, greenhouse gas analyzers require regular calibration to ensure measurement accuracy. Calibration typically involves using standard gases with known concentrations. By comparing the standard gas’s actual value with the instrument’s measurement, adjustments are made to the analyzer’s internal settings, ensuring that its measurements accurately reflect true concentrations. Calibration frequency depends on the usage and instrument type, but it is generally recommended after prolonged use or exposure to extreme environmental conditions. Some analyzers have automatic calibration functions that periodically adjust measurement accuracy, but for applications requiring high precision, manual calibration with standard gases is still necessary. Regular calibration helps to eliminate errors caused by sensor aging or environmental changes.
What precautions should be taken when using a Greenhouse Gas Analyzer?
Certain precautions should be taken when using a greenhouse gas analyzer to ensure reliable measurement data. Key considerations include:
Maintaining cleanliness
The optical sensor of the analyzer is sensitive to dust and contaminants, which can cause measurement errors, so the sensor and surrounding components should be regularly cleaned.

Avoiding temperature and humidity fluctuations
Extreme temperature and humidity may affect sensor stability and calibration. Operating the analyzer in a stable environment or using temperature and humidity regulation devices is recommended.
Regular calibration
As mentioned, regular calibration is essential for accuracy, particularly for analyzers used in scientific research and environmental monitoring, where standard gases are recommended.
Preventing interference
Strong light and electromagnetic interference may affect the measurements of optical sensors, so avoid operating the device in environments with intense lighting or electromagnetic fields.

Regular calibration
Since greenhouse gas analyzers are precision instruments, they should be stored away from extreme environments and kept in a dry, temperature-controlled space to prevent damage from vibrations.