Products/ Dilution Extractive CEMS
Dilution Extractive CEMS
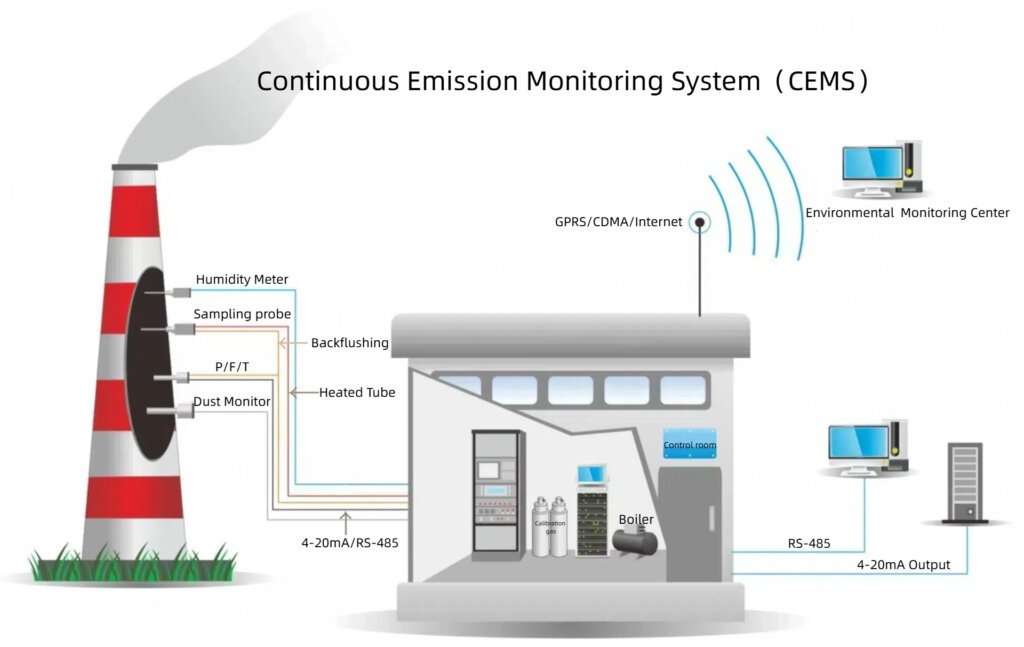
System Composition
Gaseous pollutant monitoring : SO2, NO, NO2, NOX, etc.
Flue gas parameter monitoring : flow rate, temperature, pressure, humidity, O2
System control device, data acquisition system:industrial computer

Furthermore, the optimized vapor pressure characteristics prevent interstitial condensation formation across operational temperature ranges. Even after dilution, the sample remains a wet gas, preserving its original moisture content. Thus, the measurement process is classified as a “wet-based measurement,” ensuring accurate analysis without the need for further conditioning.
Principle of chemiluminescence method:
When NO is mixed with O3 in the sample, NO2 and O2 in the excited state are generated. The excited state NO2 emits infrared light when it returns to the ground state.
NO+O3→NO2*+O2
NO2*→NO2+hv
The emission spectrum of this reaction is in the range of 600-3200 nm, and the maximum emission wavelength is 1200 nm.
3NO2 +M → 315ºC→
3NO+MoO3
The reactive emission spectrum is in the range of 400-1400 nm, and the peak wavelength is 600 nm.
Principle of pulsed fluorescence method:
When the sample is irradiated with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 190-230nm, SO2 absorbs ultraviolet light and produces an energy level transition, and SO2 changes from the ground state to the excited state, that is:
SO2+hv1→SO2*
The excited state SO2* is unstable and instantly returns to the ground state, emitting fluorescence with a peak of 330 nm, i.e
SO2*→SO2+hv2
The intensity of fluorescence is proportional to the concentration of SO2, and the concentration of SO2 can be determined by measuring the intensity of fluorescence with a photomultiplier tube and an electronic measurement system
Function: sampling, filtration, heat preservation, anti-corrosion, dilution, backflushing
Dilution ratio: 1:100
Heating temperature: 180°C
Filtration precision: 2μm
The dilution method can lead to more stable readings, resulting in less frequent calibration, saving time and resources. Many modern systems feature intuitive interfaces and automated functions that simplify operation.
This protective measure helps prolong the life of monitoring equipment, ultimately reducing maintenance and replacement costs. By diluting the gases before reaching the analyzers, the risk of damaging sensitive components is significantly reduced.
The accurate measurement and reporting capabilities of dilution extraction CEMS ensure that data submitted to regulatory agencies are reliable. Continuous monitoring allows operators to detect and address emissions issues promptly, enhancing compliance.
This technique ensures that the sample is representative of the overall emissions, allowing for precise monitoring of pollutants. By diluting the sample gas at a controlled ratio, variations in concentration that could lead to inaccuracies in measurement are minimized.
Accurate monitoring aids in identifying and mitigating excessive emissions, thereby helping to minimize environmental impact. The ability to monitor emissions precisely supports companies in their commitment to sustainable and responsible operations.
The system can be utilized in diverse industrial processes, from power generation to manufacturing, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This system effectively measures a variety of pollutants, including NOx, SO2, O2, CO, and CO2, using different analyzers tailored to specific gases.
Advantages of Dilution Extractive CEMS
The dilution system significantly enhances system reliability while reducing operational and maintenance expenses. Its average operating cost is only 1/3 to 1/2 of a direct sampling system.
Instant dilution within the probe eliminates condensation effects, removing the need for heated or insulated sampling lines. This prevents potential instrument damage caused by condensation
The accurate measurement and reporting capabilities of dilution extraction CEMS ensure that data submitted to regulatory agencies are reliable. Continuous monitoring allows operators to detect and address emissions issues promptly, enhancing compliance.
This technique ensures that the sample is representative of the overall emissions, allowing for precise monitoring of pollutants. By diluting the sample gas at a controlled ratio, variations in concentration that could lead to inaccuracies in measurement are minimized.
Rapid sample gas transmission, reduced maintenance workload, and minimal consumable usage. Additionally, it supports data processing and report generation
The system can be utilized in diverse industrial processes, from power generation to manufacturing, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This system effectively measures a variety of pollutants, including NOx, SO2, O2, CO, and CO2, using different analyzers tailored to specific gases.
The application spectrum encompasses thermal power generation, ferrous metallurgy, cement production, waste-to-energy conversion, petrochemical processing, advanced ceramics manufacturing, glass furnace operations, non-ferrous metal refining, and tobacco processing industries.
The sampling probe features a supersonic orifice that ensures a constant gas flow rate when the pressure differential across the orifice exceeds 0.46 times the upstream pressure. This condition is maintained as long as the vacuum level behind the orifice is greater than -53 kPa, regardless of changes in temperature or pressure. Venturi tube downstream of the orifice creates sufficient vacuum by directing the dilution air flow, enabling consistent gas intake. The entire process relies on aerodynamic principles, with stable operation ensured by a continuous supply of instrument air (0.6 MPa, 20 L/min).
The Venturi tube functions as a critical flow restriction mechanism, modulating dilution airflow rates. Multi-stage pressure regulation systems ensure precise pressure stabilization within the dilution air circuit, with a standard operational threshold of 0.35 kPa. Stable pressure conditions preserve homogeneous vacuum levels throughout the Venturi assembly while facilitating continuous flue gas extraction. Furthermore, this process sustains equilibrium within the integrated dilution system, thereby maintaining optimal proportional ratios.
The supersonic orifice minimizes the influence of temperature and pressure fluctuations on the dilution ratio. By operating at critical flow conditions, the orifice ensures that the volumetric flow rate of gas through it depends solely on the gas velocity, which is close to the speed of sound.
Calibration gas is introduced at the probe's front end and follows the same path as the sample gas to the analyzer. This method validates the consistency of the dilution ratio and eliminates system-wide errors, ensuring accuracy across the entire system.
The probe integrates a critical orifice (supersonic orifice) with a 0.1 µm fine filter to prevent dust blockages. 2.A Venturi tube, powered by pressurized clean air, generates the necessary vacuum. This system uses 3–7 liters of compressed air, which is directed through a nozzle to create suction, ensuring efficient and stable operation of the dilution system.
It is essential to integrate effective sample conditioning units that can remove moisture, particulate matter, and other contaminants. Maintaining appropriate temperatures within the system is vital to prevent condensation, which can skew results. Systems must be insulated and, if necessary, heated to avoid inaccuracies due to temperature fluctuations.
Standard dilution ratios, such as 100:1, may be employed to mix the flue gas with clean, dry air. This dilution must be precisely controlled to match the requirements for specific gases being detected. Incorporating adjustable dilution mechanisms allows operators to modify settings based on real-time conditions of the gas being monitored and regulatory requirements.
Analyzers must be selected for their robustness and capability to function optimally in the specific environmental and operational conditions of the facility. Different gases require distinct analytical techniques.
Incorporating self-diagnostics can alert operators to system malfunctions before they impact data collection. Designing systems that are straightforward to maintain, with easily accessible components, can help ensure technicians can perform regular checks and repairs without significant downtime
The design should facilitate continuous real-time monitoring capabilities to allow for immediate responses to emissions changes, enhancing operational control.Systems must support seamless integration with data reporting tools to ensure accurate compliance documentation can be generated without manual entry, thereby minimizing human error.
The design must consider varying environmental parameters and include features that allow the system to adapt. For instance, if ambient temperatures are prone to fluctuation, temperature-regulating equipment needs to be factored into the CEMS design. Robust Material Selection: Materials used in the construction of sampling lines, probes, and other components must be resistant to corrosion and degradation from environmental influences to enhance longevity and reliability.



| Measurement Factors | S02, NOx, 02, expandable CO, CO2 |
|---|---|
| Measurement principle | S02: Ultraviolet fluorescence method NOx: chemiluminescence method O2: zirconia |
| System Range | S02: (0~50~500)ppm Customisable NOx: (0~50~500)ppm Customisable O2: (0~25)% |
| Sampling Method | Dilution Extraction Method |
| Dilution Ratio | 1:100/1:200 Customisable |
| Zero/span drift | ±1% F.S/24h |
| Indicated value error | ±1.5% F.S |
| Response time | <120s |
| Working environment | Indoor (15~35)°C, Outdoor (-20~50)°C |
| Operating voltage | AC (220±22)V, (50±1)Hz |
| Signal output | RS232/ RS485/ (4~20) mA |